the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License.
the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License.
Aridification signatures from fossil pollen indicate a drying climate in east-central Tibet during the late Eocene
Qin Yuan
Natasha Barbolini
Catarina Rydin
Dong-Lin Gao
Hai-Cheng Wei
Qi-Shun Fan
Zhan-Jie Qin
Yong-Sheng Du
Jun-Jie Shan
Fa-Shou Shan
Vivi Vajda
Central Asia experienced a number of significant elevational and climatic changes during the Cenozoic, but much remains to be understood regarding the timing and driving mechanisms of these changes as well as their influence on ancient ecosystems. Here, we describe the palaeoecology and palaeoclimate of a new section from the Nangqian Basin in Tibet, north-western China, dated as Bartonian (41.2–37.8 Ma; late Eocene) based on our palynological analyses. Located on the east-central part of what is today the Tibetan Plateau, this section is excellently placed for better understanding the palaeoecological history of Tibet following the Indo-Asian collision. Our new palynological record reveals that a strongly seasonal steppe–desert ecosystem characterized by drought-tolerant shrubs, diverse ferns, and an underlying component of broad-leaved forests existed in east-central Tibet during the Eocene, influenced by a southern monsoon. A transient warming event, possibly the middle Eocene climatic optimum (MECO; 40 Ma), is reflected in our record by a temporary increase in regional tropical taxa and a concurrent decrease in steppe–desert vegetation. In the late Eocene, a drying signature in the palynological record is linked to proto-Paratethys Sea retreat, which caused widespread long-term aridification across the region. To better distinguish between local climatic variation and farther-reaching drivers of Central Asian palaeoclimate and elevation, we correlated key palynological sections across the Tibetan Plateau by means of established radioisotopic ages and biostratigraphy. This new palynozonation illustrates both intra- and inter-basinal floral response to Qinghai–Tibetan uplift and global climate change during the Paleogene, and it provides a framework for the age assignment of future palynological studies in Central Asia. Our work highlights the ongoing challenge of integrating various deep time records for the purpose of reconstructing palaeoelevation, indicating that a multi-proxy approach is vital for unravelling the complex uplift history of Tibet and its resulting influence on Asian climate.
- Article
(19186 KB) - Full-text XML
-
Supplement
(6267 KB) - BibTeX
- EndNote
A series of major geological events occurred during the Cenozoic, which led to a fundamental change in the global climate (Zachos et al., 2001). The most important events include the formation of the polar ice cap (e.g. DeConto and Pollard, 2003; Pagani et al., 2011), regression of the proto-Paratethys Sea from Eurasia (Abels et al., 2011; Bosboom et al., 2014; Caves et al., 2015; Bougeois et al., 2018; Kaya et al., 2019; Meijer et al., 2019), and uplift of the Qinghai–Tibetan region (Dupont-Nivet et al., 2007, 2008; Molnar et al., 2010; Miao et al., 2012; Hu et al., 2016; Li et al., 2018). Today the Tibetan Plateau (TP) is the highest elevated plateau in the world, with a complex uplift history beyond a simple collision between the Indian and Asian continents (Molnar and Tapponnier, 1975; Aitchison and Davis, 2001; Wang et al., 2008; Xia et al., 2011; Aitchison et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2012; Wang, 2014; Spicer et al., 2020). In this paper, the term “Tibetan Plateau” is used to denote the geographic extent occupied by the modern plateau, but it should not be taken to imply that an elevated expanse of low-relief topography existed across this region in the Eocene (Spicer et al., 2020).
Previous studies indicate that retreat of the proto-Paratethys Sea and the uplift of Tibet as well as other ranges to the north, such as the Altai, Sayan, and Hangay (Caves et al., 2014), may have been responsible for monsoon intensification and aridification across the Asian continental interior in the Paleogene, although the timing of these mechanisms, and their roles in forcing climate dynamics, are still debated (Caves et al., 2015; Spicer, 2017). In particular, a lack of consensus exists regarding the onset of Asian aridification, whether it was a Paleogene or Neogene phenomenon, and its relationship with Tibetan uplift (e.g. Dupont-Nivet et al., 2007; Xiao et al., 2010; Miao et al., 2012; Caves et al., 2015; Liu et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2018; L. Li et al., 2019; Paeth et al., 2019). Aridification in north-eastern Tibet appears to have intensified after the middle Eocene climatic optimum (MECO; 40 Ma), a short-lived warming event documented in marine records globally. The drying climate after this event is primarily linked to the second regression of the proto-Paratethys Sea, which reduced moisture supply via the westerlies to Central Asia (Kaya et al., 2019). In north-eastern Tibet, the regional disappearance of perennial lakes, accompanied by an increase in pollen from xerophytic plants, marks a permanent aridification step in the Asian terrestrial record after ∼40 Ma (Bosboom et al., 2014); however, these climatic trends are yet to be identified in central Tibet.
The uplifting, large-scale thrusting, and striking of Tibet caused several Paleogene intra-continental basins to form within the northern and central Qinghai–Tibetan region, including the Nangqian Basin. Situated in the Yushu area (Fig. 1), this basin lies directly above the Lhasa Terrane, which comprised part of north-eastern Gondwana in the Late Triassic to Early Jurassic and formed through a subduction–accretion process similar to that of the later Indo-Asian collision (Liu et al., 2009). Subsequent to its formation, the Nangqian Basin was infilled with non-marine sedimentary deposits (Wang et al., 2001, 2002), and it is now a key site for understanding the Cenozoic tectonics, palaeoelevational, and palaeoclimatic changes that have taken place in the Qinghai–Tibetan region since the collision of the Indian and Asian tectonic plates (Gupta et al., 2004; Molnar, 2004; Wang et al., 2001). Previous palynological studies from this part of the plateau have revealed a relatively dry climate with brief humid intervals in the late Eocene, dominated by drought-tolerant (xerophytic) and salt-tolerant (halophytic) steppe–desert vegetation (Wei, 1985; Yuan et al., 2017).
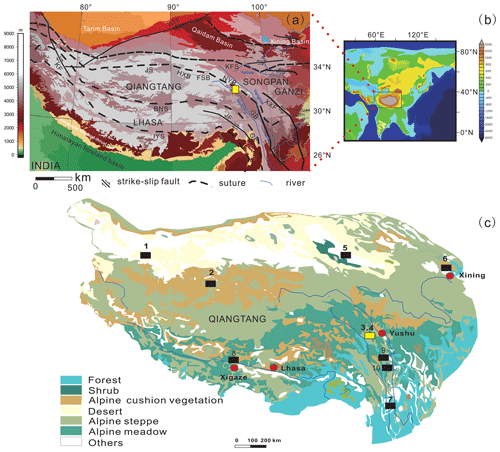
Figure 1(a) Tectonic map of the Tibetan Plateau (TP) indicating the major sedimentary basins (HXB: Hoh Xil Basin; FSB: Fenghuo Shan basins; NYB: Nangqian-Yushu basins; GB: Gongjo Basin), sutures (JS: Jinsha Suture; BNS: Bangong-Nujiang Suture; IYS: Indus-Yalu Suture), and major faults (KF: Karakorum Fault; ATF: Altyn Tagh Fault; KFS: Kunlun Fault system; XXF: Xiangshuihe–Xiaojiang Fault system; RRF: Red River Fault; GF: Gaoligong Fault; JF: Jiali Fault), redrawn following Horton et al. (2002). The yellow rectangle indicates the location of this study in the Nangqian Basin. (b) A late-middle Eocene (40 Ma) palaeogeographic reconstruction, with the Qinghai–Tibetan region indicated by a black rectangle (redrawn following Tardif et al., 2020). (c) Modern vegetation distributions on the Tibetan Plateau, with major towns indicated in red (redrawn following Baumann et al., 2009). Numbers indicate the positions of palynological assemblages that are correlated in Fig. 4 and the text: 1, Tarim Basin; 2, Hoh Xil Basin; 3 and 4, Nangqian Basin (this study is indicated by a yellow rectangle); 5, Qaidam Basin; 6, Xining Basin; 7, Jianchuan Basin; 8, Xigaze Basin; 9, Markam Basin; and 10, Gonjo Basin.
This climate and palaeoflora were very similar to contemporaneous plateau ecosystems further to the north, such as the Xining (Dupont-Nivet et al., 2007, 2008; Hoorn et al., 2012) and Hoh Xil (Liu et al., 2003; Miao et al., 2016) basins, demonstrating the potential for these successions to be biostratigraphically correlated. Furthermore, oxygen isotope records indicate that both northern and east-central Tibet received moisture dominantly via the westerlies, which have maintained a semi-arid to arid climate in Central Asia since the early Eocene (Caves et al., 2015; Caves Rugenstein and Chamberlain, 2018). This suggests that aridification across this part of Tibet in the Eocene was related to large-scale atmospheric transport and justifies a comparison of palynological records in the northern and central parts of the TP.
In contrast, south-eastern Tibet seems to have experienced a more humid climate hosting widespread conifer and warm-temperate broad-leaved forests (Li et al., 2008; Su et al., 2018), likely influenced by a Paleogene intertropical-convergence-zone-driven monsoon system similar to the modern Indonesia–Australia monsoon (I-AM; Spicer, 2017). Today this wet-summer, dry-winter monsoonal regime presides over a biodiversity hotspot in southern Asia; similarly seasonal climates in the past are thought to also have stimulated high biodiversity (Spicer, 2017). Southerly moisture has probably rarely extended northward of the central TP (Caves Rugenstein and Chamberlain, 2018); moreover, southern Tibetan Eocene floras display a modern aspect (e.g. Linnemann et al., 2018) that is quite different to more ancestral steppe vegetation hosted in the northern TP.
The extent and timing of mechanisms that promoted somewhat different floras south and north of the Tibetan–Himalayan orogen remain poorly understood, with Licht et al. (2014) reporting marked monsoon-like patterns in both regions during the Eocene, utilizing records from north-west China and Myanmar. The role of Qinghai–Tibetan uplift also remains unclear, with contrasting models of plateau evolution supported by various tectonic, isotopic, modelling, and biological evidence (e.g. Mulch and Chamberlain, 2006; Rowley and Currie, 2006; Ding et al., 2014; Li et al., 2015; Jin et al., 2018; Botsyun et al., 2019; Su et al., 2019; Valdes et al., 2019; Shen and Poulsen, 2019; and summaries in Spurlin et al., 2005; Wang et al., 2014; and Spicer, 2017). Accordingly, further stratigraphic and palaeoenvironmental studies of the sedimentary successions within these basins are necessary to provide clarification on local vs. regional climatic changes experienced as a result of uplift, global cooling, and progressive aridification in Central Asia during the Paleogene.
The location of the Nangqian Basin on the east-central part of the TP provides an ideal locality for testing the influence of these mechanisms on Asian palaeoenvironments and climates. We selected the Ria Zhong (RZ) section in the Nangqian Basin for palynological analyses and correlated this section with previous studies from this and other TP basins. These new results better constrain the biostratigraphy of Paleogene successions across the plateau, and they provide new information on the depositional environment as well as the elevational and climatic changes in eastern Tibet during the Eocene. We further synthesize results previously published in Chinese journals, making these results accessible for an international audience.
The Nangqian Basin is located on the border between Qinghai Province and the Tibet Autonomous Region at an elevation of approximately 4500–5000 m and is characterized by a continental seasonal monsoon climate, with long, cold winters, and short, rainy, and cool to warm summers (Yuan et al., 2017). Most of the annual precipitation occurs from June to September, when, on average, most days in each month experience some rainfall (Qinghai BGMR, 1991). The region presently hosts alpine steppe and meadow (Fig. 1) characterized by Cyperaceae, Asteraceae, Amaranthaceae, and Poaceae, as well as conifer and broad-leaved forests dominated by conifers such as Pinus, Picea, Abies, Tsuga, and deciduous angiosperms such as Quercus (oak) and Betula (birch), although intensive logging has markedly contracted these forests to steep slopes and remote areas (Herzschuh, 2007; Baumann et al., 2009).
Although the timing of the Indo-Asian collision remains uncertain (e.g. Xia et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2012; Wang et al., 2014), its initiation formed north-eastward extrusion facilitated by motion along a series of contraction deformation and strike-slip faults in eastern Tibet, including the Yushu–Nangqian thrust belt and the Jinshajiang strike-slip fault system (Fig. 1; Hou et al., 2003; Yin and Harrison, 2000; Spurlin et al., 2005). The Nangqian Basin is one of four sedimentary basins in the Yushu–Nangqian region that formed during Paleogene contraction (Horton et al., 2002), it is ∼80 km long in the south–north direction and 15 km wide in the east–west direction and is situated in the eastern part of the Qiangtang Terrane (Fig. 1; Hou et al., 2003). The tectonic evolutionary history of the area includes an early-stage extrusion thrust foreland basin, a middle-stage strike-slip foreland basin, and the late-stage extrusion strike-slip foreland basin (Wang et al., 2001, 2002; Mao, 2010; Jiang et al., 2011).
Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Paleogene sedimentary rocks exposed along the Yushu–Nangqian traverse include Carboniferous–Triassic marine carbonates and minor clastic units overlain by Jurassic, Cretaceous, and Paleogene red beds (Liu, 1988; Qinghai BGMR, 1991). The southern area mainly comprises the Carboniferous Zhaduo Group (C1zd), whereas the northern area is dominated by younger strata comprising the Upper Triassic Jieza Group (T3jz; Qinghai BGMR, 1991). Our study concentrated on the Cenozoic gypsum-bearing Gongjue Formation, which unconformably overlies Carboniferous–Triassic rocks and may be conformable with underlying Upper Cretaceous strata (Qinghai BGMR, 1983a, b, 1991). It is divided into five lithological units (Eg1–Eg5), from bottom to top (Du et al., 2011). Eg1 comprises shallow lacustrine facies reaching a thickness of ca. 400 m, which lie unconformably on a basement of Carboniferous–Permian sedimentary rocks. The strata in units Eg2, Eg4, and Eg5 were mainly formed in an alluvial environment with rapid sedimentation rates, with strata reaching a thickness of ca. 530, 1100, and 2500 m respectively.
The focus of this study is the Eg3 unit which has a more complex depositional history; it is the thickest (reaching 3500 m) of the five units and the most widely distributed unit in the Nangqian Basin. Eg3 is divided into three members: (1) the Ri'Anongguo conglomerate member, which reaches a thickness of approx. 1300 m; (2) the Dong Y'ru sandstone member with limestone beds, which reaches a thickness of 700–1000 m; and (3) the uppermost Gouriwa member, comprising mudstones (generally developed as red beds) intercalated with gypsum and reaching 900–1200 m in thickness (Wang et al., 2002). This latter member has been interpreted as being deposited in a fluviolacustrine environment under a range of climatic conditions (Wang et al., 2001, 2002; Jiang et al., 2011). Note that the stratigraphic framework for the Gongjue Formation described in Yuan et al. (2017) is incorrect, referring to the three members above as comprising the entire Gongjue Formation instead of only the Eg3 unit within the Gongjue Formation; we correct this here based on the descriptions of Wang et al. (2001, 2002) and Du et al. (2011). Based on palynological analyses and ostracod assemblages, the mudstone-dominated successions of the Eg3 unit have been dated as late Eocene to Oligocene in age (Wei, 1985; Yuan et al., 2017), which is corroborated by 38–37 Ma 40Ar/39Ar ages from interbedded volcanic rocks in the uppermost strata of the Nangqian Basin (Spurlin et al., 2005).
Although few palynological data currently exist from the Nangqian Basin (Wei, 1985; Yuan et al., 2017), palynology has been extensively applied for biostratigraphic purposes, as well as to infer Cenozoic climatic changes, in basins across the TP, including the Qaidam Basin (Xu et al., 1958; Zhu et al.,1985; Wang et al., 1999; Sun et al., 2005; Lu et al., 2010; Ji et al., 2011; Miao et al., 2011, 2012, 2013a; Cai et al., 2012; Herb et al., 2015; Wei et al., 2015), the Xining Basin (Dupont-Nivet et al., 2008; Miao, 2010; Hoorn et al., 2012; Miao et al., 2013b; Bosboom et al., 2014), the Hoh Xil Basin (Liu et al., 2003; Miao et al., 2016), the Tarim Basin (Sun et al., 1999; Zhu et al., 2005; Bosboom et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2013), the Jianchuan Basin (L. Li et al., 2019), and the Xigaze region of Tibet (Li et al., 2008). Most of these studies are limited to the sedimentary successions within the foreland basins of the northern TP, rendering it important to gather further data on central Tibetan basins that preserve a complex sequence of Cenozoic deformation in relation to the Indo-Asian collision zone (Spurlin et al., 2005). Furthermore, correlation of the above-mentioned northern successions with our new section from the Nangqian Basin (presented in Sect. 5.1) is valuable for advancing understanding of differences in vegetational composition across the TP, as well as the palaeoenvironmental and climatic signals recorded by these ecosystems.
In this study, the RZ section located in the north-western part of the Nangqian Town (N32∘12′10′′, E96∘27′19.42′′; altitude 3681 m) was sampled for sedimentological and palynological analyses (Fig. 2). The RZ section is a ca. 260 m thick portion of the Gongjue Formation where it represents the uppermost Gouriwa member of the Eg3 unit. The sediments mainly comprise lacustrine facies represented by red mudstones and siltstones, intercalated with gypsum beds. A more detailed description of the sedimentology, geochemistry, and palynofacies of the section are presented in a separate paper (Yuan et al., 2020). A total of 71 palynological samples were collected from mudstones or fine-grained siltstones.
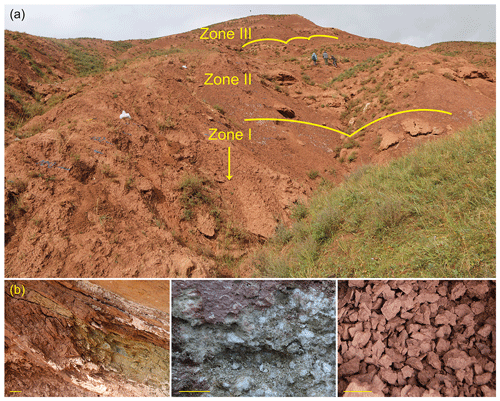
Figure 2(a) Field photograph of the newly sampled Ria Zhong (RZ) section with palynological zones marked. The section is located in the Nangqian Basin, Yushu area, Tibet (N32∘12′10", E96∘27′19.42"; altitude 3681 m), and it represents the uppermost Gouriwa member of the Eg3 unit in the Cenozoic Gongjue Formation. The lithostratigraphy and geochemistry of the RZ section are further described in Yuan et al. (2020). (b) Field photographs showing representative lithologies in the RZ section (from left to right): intercalated siltstone and mudstone, massive gypsum, silty mudstone. The scale bar represents 5 cm.
The samples were first treated with 36 % HCl and 39 % HF to remove carbonates and silicates and then sieved through a 10 µm nylon mesh. Subsequently, the residue was density separated using ZnCl2 (density = 2.1). The organic residue was mounted on microscopic slides in glycerin jelly. All slides were examined at the Swedish Museum of Natural History under a Leica light microscope (OLYMPUS BX51), and micrographs were taken of selected specimens. As is standard for palynostratigraphic studies, we primarily used light microscopy (LM) to identify, count, and photograph palynomorphs present in the samples. An ESEM FEI Quanta FEG 650 scanning electron microscope (SEM) was used to obtain additional detailed surface images of Ephedripites subgenus Ephedripites and Ephedripites subgenus Distachyapites, hereafter indicated as Ephedripites (Ephedripites) and Ephedripites (Distachyapites), and other key species. Slides and residues are hosted at the Swedish Museum of Natural History, Stockholm, Sweden.
From each of the 21 productive samples >200 grains were identified and counted, and the pollen diagrams (Figs. 3, S1, S2) were plotted using TGView© and Tilia© 2.0 software (Grimm, 1991). We assigned fossil pollen taxa to ecological groups or plant functional types (PFTs) according to their correspondence with nearest living relatives (NLR) in modern Asian biomes (following the taxon-to-NLR assignments of Hoorn et al., 2012). PFTs are shown in the supplementary dataset of Yuan and Barbolini (2020) as well as Figs. S1 and S2. Statistical analysis of the palynological assemblages was conducted using CONISS (constrained incremental sums of squares cluster analysis), a multivariate agglomerative method for defining zones hierarchically (Grimm, 1987). A stratigraphically constrained analysis was performed on pollen-percentage values with square root transformation (the chord distance of Cavalli-Sforza and Edwards, 1967) which up-weights rare variables relative to abundant ones; therefore, this method is particularly appropriate for pollen datasets (Grimm, 1987). Results of the CONISS ordination on all taxa were presented as a dendrogram onto the pollen diagram (Fig. S1), and the ordination was then repeated to test the robustness of the stratigraphic zones by excluding the “Other/Unknown/Unresolved NLR” ecological group. Very similar zones were retained in the new cluster analysis (Fig. S2), increasing confidence that these zones represent true changes in vegetation and climate dynamics recorded throughout the section. Both CONISS ordinations were used in conjunction with the taxonomic and quantitative composition of the palynological assemblage in order to demarcate zones and subzones within the section.
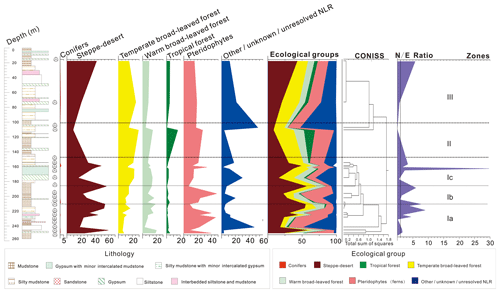
Figure 3Cumulative pollen summary diagram of the Ria Zhong (RZ) section in the Nangqian Basin, Yushu area, Tibet, with palynomorph percentages of the total pollen sum plotted on the x axis as well as zones and subzones based on CONISS ordinations. Pollen taxa are grouped into plant functional types (PFTs) according to their correspondence with nearest living relatives (NLR), indicated in the legend. Some taxa have multiple or unresolved botanical affinities and are, therefore, assigned to the “Other/unknown/unresolved NLR” group. Productive horizons are indicated by a small trilete spore to the right of the simplified section log. The Nitraria/Ephedra (N∕E) pollen ratio is plotted in purple, with a dashed line indicating the transition point between desert/semi-desert ecosystems (<1) and steppe–desert (>1).
Recovery of palynomorphs was generally poor, particularly in the upper part (0–147 m) of the section. Although there is no direct linkage between the productivity of pollen samples and lithofacies, evidence of increasing aridity is preserved in the upper part of the section through both the palynological and sedimentological records. Accordingly, vegetation biomass was likely lower in these more arid environments, and extended exposure on the landscape before burial can destroy palynomorphs; both of these factors are likely contributors to the lower productivity observed. In total, only 21 productive samples were obtained from 71 processed samples, indicating a productivity ratio of 30 %. Nevertheless, individual well-preserved palynological assemblages were recovered throughout the section, enabling a representative portrayal of vegetation changes through time to be reconstructed. In total 26 spore and 81 pollen taxa (5 gymnosperm and 76 angiosperm morphospecies) were able to be identified, which are illustrated (Plates 1, 2, and 3) and grouped into seven different plant functional types (PFTs) that represent various ecological groups (Fig. 3). Overall trends for the RZ section include rare conifers and a general dominance of steppe–desert pollen in all zones. Ferns are abundant and diverse, particularly in the lower part of the section (Zone I), while temperate and warm broad-leaved forest are relatively diverse and present throughout, although not particularly abundant in any zone. Steppe–desert pollen decreases concurrently with a spike in tropical forest pollen in one sample from Zone II, and it then resurges to dominance in Zone III. Palynological zones are marked on the field photograph of the RZ section (Fig. 2) and plotted on the pollen diagrams (Figs. 3, S1, S2).
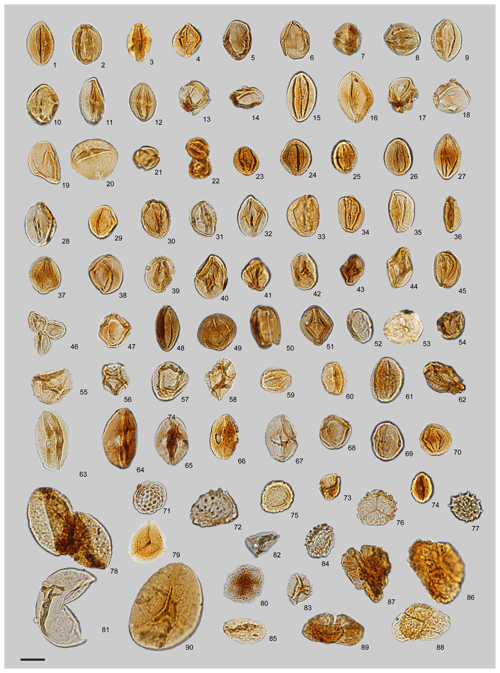

Plate 1Light micrographs of selected pollen grains and spores from the Ria Zhong (RZ) section, Nangqian Basin: 1–12, Nitrariadites/Nitraripollis; 13–20, Meliaceoidites; 21–25, Qinghaipollis; 26–32, Rhoipites; 33–36, Labitricolpites; 37–45, Quercoidites; 46, Quercoidites minutus; 47–51, Rutaceoipollenites; 52–54, Momipites; 55–58, Fupingopollenites; 59–61, Ilexpollenites; 62, Aceripollenites; 63–67, Euphorbiacites; 68–69, Faguspollenites; 70, Retitricolporites; 71, Chenopodipollis; 72, Echitriporites sp.; 73, Sporopollis; 74, Caprifoliipites / Oleoidearumpollenites; 75–76, Pterisisporites; 77, unidentified baculate spore; 78, Liliacidites; 79–80, Pterisisporites; 81, Taxodiacites; 82–83, Deltoidospora; 84, Lycopodiumsporites; 85, Spinizonocolpites; 86–88, Verrucosisporites; and 90, Lygodiumsporites. The scale bar represents 10 µm.
While the generally high proportion of spores suggests a significant proportion of local deposition (at site), as a whole the palynological assemblages are taken to reflect the regional vegetation, and they may also include some taxa that are prone to longer-distance transport. These latter taxa are mostly trees and are normally present in small percentages except for Pinus, which can comprise 10 %–50 % in the palynological records of deserts and steppe–deserts (but is extremely rare in our section; Ma et al., 2008; Hoorn et al., 2012). Studies on the correspondence between the modern pollen rain and regional vegetation on the Tibetan Plateau indicate generally good agreement and confirm that the use of palynology for palaeoenvironmental reconstruction in deep time is therefore also appropriate (Cour et al., 1999; Li et al., 2020).
4.1 Stratigraphic zonation based on palynology
Based on the results of two CONISS ordinations combined with the taxonomic and quantitative composition of the palynological assemblage (see Sect. 2; Figs. 3, S1, S2), the succession was divided into three zones (I, II, and III) of which Zone I was further divided into three subzones (a, b, and c), all of which demonstrate unique vegetation dynamics within that zone. Important trends for each zone and subzone are described below. The zone boundaries are positioned at the upper limit of the samples that mark each boundary. A complete overview of the raw counts, percentages, and arithmetic means are given in the Supplement.
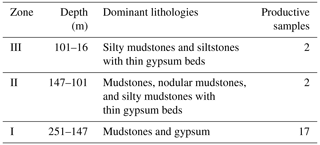
4.1.1 Zone I (17 samples, 251–147 m)
Conifers in this zone are rare, represented only by Taxodiacites (Cupressaceae) and Tsugaepollenites (Pinaceae), and never comprise more than 3 %. The assemblage is dominated by steppe–desert taxa, which together comprise nearly 40 % and include numerous types of Ephedripites (Plate 2), Nitrariadites/Nitraripollis, and Qinghaipollis, as well as rarer xerophytic taxa such as Chenopodipollis and Nanlingpollis. The second most abundant group is the Pteridophytes (ferns), which is also the most diverse of all the groups represented in the RZ section. Broad-leaved forest forms a minor component of the palynological record, with warm forest being more abundant than temperate forest and represented primarily by Rutaceoipollenites. Tropical forest pollen is rare, and includes Spinizonocolpites and Fupingopollenites. Some pollen types have unresolved botanical affinities or affinities with multiple ecological groups, and these are grouped separately but do not provide ecological information.

Plate 2Light micrographs of ephedroid pollen from the Ria Zhong (RZ) section, Nangqian Basin: A, Ephedripites (Distachyapites) cheganica; B, Ephedripites (Distachyapites) fusiformis; C1–C4, Ephedripites (Distachyapites) megafusiformis; D1–D2, Ephedripites (Distachyapites) eocenipites; E1–E3, Ephedripites (Distachyapites) nanglingensis; F, Ephedripites (Distachyapites) obesus; G, Ephedripites (Ephedripites) bernheidensis; H, Ephedripites (Ephedripites) montanaensis; I, Ephedripites (Ephedripites) sp. 2 (Han et al., 2016); J, Ephedripites (Ephedripites) sp. a; K, Ephedripites (Ephedripites) sp. b; L, Steevesipollenites cf. S. binodosus; and M, Steevesipollenites jiangxiensis. The scale bar represents 10 µm.
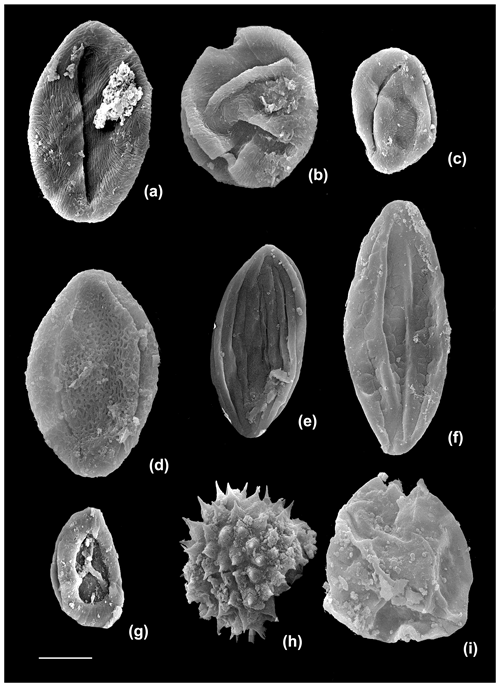
Plate 3Scanning electron microscope (SEM) photographs of selected fossil taxa in the Ria Zhong (RZ) section, Nangqian Basin: (a, b, c) Nitrariadites/Nitraripollis; (d) Retitricolporites; (e) Ephedripites (Ephedripites) sp. 2 (Han et al., 2016); (f) Ephedripites (Distachyapites) eocenipites; (g) Pterisisporites; (h) unidentified baculate spore; and (i) Momipites. The scale bar represents 10 µm.
Zone I is divided into three subzones on the basis of abundance patterns among particular palynomorph taxa. Subzone Ia (nine samples, 251–209 m) is unique in that Ephedripites (steppe–desert group), Cupuliferoipollenites (temperate broad-leaved forest), and Rutaceoipollenites (warm broad-leaved forest) are more abundant than in other subzones of Zone I, whereas Momipites/Engelhardthioipollenites (warm broad-leaved forest) is less abundant, and Aceripollenites + Faguspollenites (temperate broad-leaved forest) are very rare compared with the remainder of Zone I. Of the entire section, Caryophyllidites (steppe–desert) only occurs in Subzone Ib (three samples, 209–187 m), which also records a spike of Momipites/Engelhardthioipollenites (warm broad-leaved forest). Subzone Ic (five samples, 187–147 m) contains the greatest proportion of Nanlingpollis (steppe–desert) in the entire section as well as spikes of Aceripollenites + Fraxinoipollenites (temperate broad-leaved forest), while Qinghaipollis (steppe–desert) and ferns decrease in this subzone.
4.1.2 Zone II (two samples, 147–101 m)
No conifer pollen occurs in this zone, and on average, the steppe–desert taxa Ephedripites (gymnosperm), Nitrariadites/Nitraripollis, and Qinghaipollis (angiosperms) are far less abundant than in other parts of the section (average of 9 % in Zone II vs. 38 % in Zone I and 32 % in Zone III). However, a spike in the ancestral (old) Ephedra type is observed during Zone II, which is not observed in the other zones or later in the Eocene (Yuan et al., 2017). Notably, tropical forest pollen increases markedly in one sample from this zone (as regional input), comprising mostly Fupingopollenites, while temperate broad-leaved forest (Aceripollenites, cf. Caprifoliipites) and warm broad-leaved forest (Rutaceoipollenites) are also more prevalent. Pollen of unknown or multiple affinities is higher in this zone and is reflected by spikes of Labitricolpites and Rhoipites. A low recovery of productive samples was obtained from this zone; thus, the above-described trends may reflect an incomplete picture of environmental changes during this interval.
4.1.3 Zone III (two samples, 101–16 m)
Conifers in this zone are very rare, represented only by Tsugaepollenites. Steppe–desert taxa again dominate this zone, with Nitrariadites/Nitraripollis increasing steadily through the section. Temperate broad-leaved forest is now much more common than warm broad-leaf or tropical forest pollen, while ferns are least common in this zone but still plentiful. A low recovery of productive samples was obtained from this zone; thus, the above-described trends may reflect an incomplete picture of environmental changes during this interval.
5.1 Age assignment
Age constraints for the RZ section are provided by the K–Ar ages from shoshonitic lavas and felsic and porphyry intrusions that are either interbedded with, or unconformably overlie, the lacustrine to alluvial Nangqian strata. Emplacement ages across the Nangqian Basin vary between 32.04 and 36.5 Ma (Deng et al., 1999); 37.0±0.2 Ma and 38.2±0.1 Ma (Spurlin et al., 2005); 37.1 and 37.8 Ma (Zhu et al., 2006); and 35.6±0.3 and 39.5±0.3 Ma (Xu et al., 2016). In the latter study, zircon U–Pb age data were derived from felsic intrusions sampled at two localities in the Nangqian Basin (Boza and Nangqian). The syenite porphyries from the Boza area (further south of the RZ section) show an emplacement age of 35.58±0.33 Ma, whereas the monzonite porphyries from the Nangqian area (just south-east of the RZ section) have older magmatic emplacement ages, ranging from 39.5±0.3 Ma to 37.4±0.3 Ma. As this age range is broadly coeval with the age of the mafic volcanic rocks in the Nangqian Basin (37.0–38.2 Ma; Spurlin et al., 2005) as well as the age range obtained by Zhu et al. (2006), here we consider ∼37–38 Ma to represent a minimum age for the RZ section. This is also congruent with palynological evidence for the overall age of the sampled strata (Fig. 4), which is discussed in more detail below.
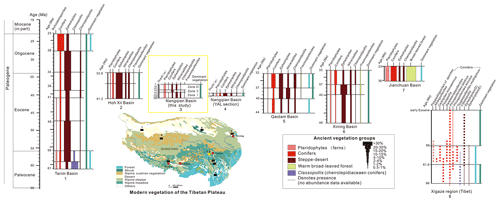
Figure 4Palynozonation of the Paleogene successions across the northern, central, and southern Tibetan Plateau, with the numbers under each section indicating the associated basin: 1, Tarim Basin (Wang et al., 1990a, b); 2, Hoh Xil Basin (Miao et al., 2016); 3 and 4, Nangqian Basin (this study; Yuan et al., 2017); 5, Qaidam Basin (Zhu et al., 1985; Zhang, 2006; Miao et al., 2016); 6, Xining Basin (Wang et al., 1990a, b; Hoorn et al., 2012); 7, Jianchuan Basin (Wu et al., 2018); and 8, the Xigaze region (Li et al., 2008). The dominant ancient vegetation reconstructed from palynological assemblages is shown to the right of each section. The modern vegetation map was redrawn from Baumann et al. (2009).
The assemblage from the RZ section is very similar to those from the Yang Ala section in the Nangqian Basin, dated as late Eocene (Yuan et al., 2017), the Eocene Wuqia assemblage (site 98) from the west Tarim Basin (Wang et al., 1990a, b), the late-middle Eocene to late Eocene assemblage from the upper Niubao Formation, the Lunpola Basin (Song and Liu, 1982; J. G. Li et al., 2019), and the Bartonian (41.2–37.8 Ma) part of the palynological record in the Xining Basin (Dupont-Nivet et al., 2008; Hoorn et al., 2012; Han et al., 2016). Specifically, the absence of Classopollis, Exesipollenites, and Cycadopites combined with the predominance of Nitrariadites/Nitraripollis and Ephedripites pollen, and the presence of the middle Eocene–Neogene genus Fupinggopollenites (Liu, 1985), indicates that the RZ section cannot be older than middle Eocene (Fig. 4). It is also unlikely to be of latest Eocene age or younger due to the lack of significant conifers that become more common approaching the Eocene–Oligocene Transition (Hoorn et al., 2012; Page et al., 2019; Fig. 4). Specific ranges and abundance patterns of these and other key taxa within Eocene Tibetan basins (Figs. 4 and 5) enable the age of the section to be better constrained, which is explored in greater detail below.
Ephedra is a gymnosperm shrub with the oldest macrofossils from the Early Cretaceous (Bolinder et al., 2016; Han et al., 2016), but the genus is probably older, dating to the Triassic (Yang, 2002; Sun and Wang, 2005) or even the Permian (Wang, 2004) based on the ephedroid pollen record. Its current distribution is limited primarily to arid and semi-arid regions of the world (Stanley et al., 2001), and the fossil pollen representative, Ephedripites, is widespread in Cenozoic evaporates, indicating the xerophytic nature of this genus (Sun and Wang, 2005). The Xining Basin in northern Tibet records a particularly time-extensive section with good age control (Dupont-Nivet et al., 2008; Hoorn et al., 2012; Meijer et al., 2019) that reveals a detailed pattern of changes in Ephedripites pollen during the middle–late Eocene. After 38.8 Ma, Ephedripites comprised ca. 20 %–60 % of the total palynological composition in the Xining Basin, with a predominance of the derived type, Ephedripites (Distachyapites) (Han et al., 2016). Prior to this (ca. 41–38.8 Ma), the record comprised a mix of the derived type; the ancestral type, Ephedripites (Ephedripites); and another ephedroid genus, Steevesipollenites (Han et al., 2016; Bolinder et al., 2016). A similar pattern is observed in the Nangqian Basin, with a spike of the ancestral type of Ephedra only recorded in Zone II and not observed in the rest of the RZ section or elsewhere in the Nangqian Basin (Yuan et al., 2017). This suggests a correlation between Zone I of the Xining Basin and Zone II of the RZ section (Fig. 5). As it is possible that the change in Ephedripites diversity may not have occurred across Tibet simultaneously (i.e. at ∼39 Ma), we suggest that this most likely constrains the age of the RZ section to late Eocene (Bartonian; 41.2–37.8 Ma).
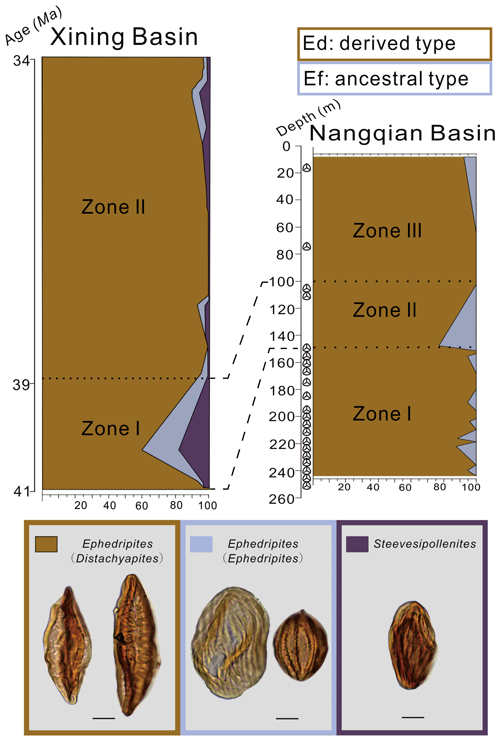
Figure 5Eocene ephedroid pollen composition in the Xining (north-eastern TP) and Nangqian (east-central TP) basins, illustrating the distributions of Ephedripites (Ephedripites) (ancestral type; “Ef”), Ephedripites (Distachyapites) (derived type; “Ed”), and Steevesipollenites. Productive horizons for the Ria Zhong (RZ) section are indicated by a small trilete spore to the right of the marked depths.
In addition to the proportions of the ancestral vs. derived type of Ephedripites, a significant spike in tropical forest pollen in one sample at this time, combined with a large decrease in steppe–desert pollen, suggests that Zone II of the RZ section reflects a temporary warming interval in the Eocene. Although the increase in tropical forest taxa in one sample from this zone does not indicate an actual biome shift in the Nangqian region from “steppe” to “tropical forest”, it suggests a change in regional climate through increased input of regional tropical taxa. This could possibly be concurrent with the MECO (∼40 Ma), a transient warming event that preceded rapid aridification in Central Asia (driven primarily by proto-Paratethys Sea retreat; Kaya et al., 2019). This interval is followed by a change in lithofacies (decreasing thickness of gypsum beds) and an increase in steppe–desert pollen records in north-western China (Bosboom et al., 2014). Similar trends are also observed in the Nangqian Basin (Fig. 3), suggesting a possible correlation. However, it must be considered that the upper zones of the RZ section yielded a low number of samples (zones II and III each comprise only two samples), and the tropical forest spike is only present in one of these samples. This places statistical limitations on the interpretations that can be drawn; therefore, further investigations should be made in Nangqian and other parts of Tibet to corroborate this finding. Accordingly, for the moment we do not date the RZ section on the basis of a tentative correlation to the MECO at ∼40 Ma; however, available evidence does suggest that the spike of tropical forest represents a temporary shift in regional climate. The palynomorphs from these samples were not degraded nor compressed to a greater degree than palynomorphs from the rest of the section, and they were of a similar colour and appearance, suggesting it is unlikely that the pollen in Zone II represents reworking or contamination. Furthermore, the increase in tropical forest taxa is accompanied by a large decrease in steppe–desert pollen which is not observed in the other zones of this section (average 9 % steppe–desert pollen in Zone II vs. 38 % in Zone I and 32 % in Zone III), nor later in the Eocene in the Nangqian Basin (Yuan et al., 2017). This further indicates a temporary shift in the regional climate to warmer and wetter at this time.
In northern Tibet, Pinaceae (conifers) abruptly increased in the palynological record at 36.55 Ma (Page et al., 2019), which is not observed in the RZ section. The rare conifers in this latter assemblage are in accordance with the minimum depositional age constraints of ∼ 37–38 Ma from overlying volcanic rocks. In conjunction with the palynostratigraphic correlations from across Tibet (Fig. 4), as well as the change in the proportions of the ancestral vs. derived type of Ephedripites (Fig. 5), the age of the complete section is proposed to be Bartonian (41.2–37.8 Ma; Figs. 4, 5).
5.2 Palaeoclimate
The RZ section records three distinct palaeofloras in east-central Tibet that evolved in response to changing climate in the Eocene (Fig. 6). During deposition of Zone I, the climate was warm, and vegetation was characterized by steppe–desert shrubs, diverse ferns, and a lesser component of temperate and warm broad-leaved forest. Interestingly, prominent vegetation groups with very different moisture requirements existed within a limited distance of each another in the Nangqian area. A very diverse and abundant pteridophyte (fern) community as well as conifers such as Taxodiacites and Tsugaepollenites would have required higher humidity (e.g. Kotthoff et al., 2014), but the abundant halophytic and xerophytic steppe–desert vegetation would likely only have been competitive in arid environments. The dominant plants belonging to these salt- and drought-tolerant groups (Nitraria and Ephedra) grow today in Central Asian regions with a mean annual precipitation (MAP) of 100 mm or less, and they are also associated with arid palaeoenvironments through the Cenozoic (Sun and Wang, 2005). Although the conifers (produced by cypress and Tsuga) could have been windblown from further distances, the coexistence of such diverse and abundant ferns and steppe–desert vegetation in the landscape (PFTs with opposing moisture requirements for competitiveness) has not been observed in other Tibetan basins to date (Miao et al., 2016, Table 1); therefore, it does not seem to reflect conventional spatial patterning of less water-dependant vegetation growing upland. Rather, it may suggest an environment with strongly seasonal precipitation that would favour lush vegetation growth for a restricted interval and, alternately, xerophytic vegetation during the dry season.
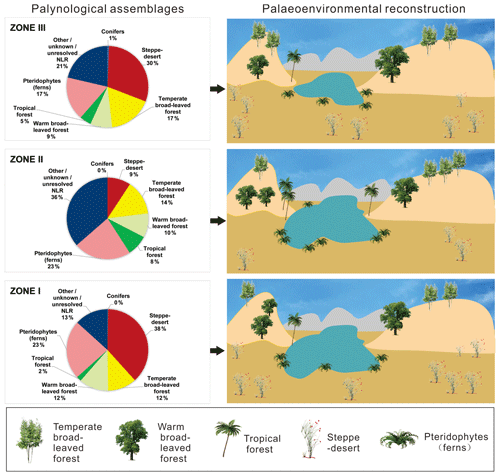
Figure 6Palaeoenvironmental reconstruction of the Nangqian area, illustrating the three distinct floral assemblages recovered from the RZ section. Vegetation during deposition of Zone I was dominated by steppe–desert shrubs, which decreased sharply in Zone II in conjunction with a spike in tropical forest. Afterwards the basin became drier and steppe–desert vegetation again dominated the landscape.
Table 1Lithologies of the palynological zones identified within the Ria Zhong (RZ) section in the Nangqian Basin, Yushu area, Tibet. Information is given on the stratigraphic horizons of each zone, its dominant lithologies, and the total number of productive palynological samples that were obtained.
Based on a comparison of existing palynofloral records with our new section, the northern regions of the plateau (Tarim, Qaidam, Hoh Xil, and Xining basins) were already significantly more arid than the central TP in the middle Eocene, having hosted greater proportions of xerophytic plants (Fig. 4). Therefore, precipitation in the greater Nangqian region would have been unlikely to derive from the westerlies, which served as the dominant moisture source northward of the central TP since at least the early Eocene (Caves et al., 2015). This suggests that the central TP could have instead been influenced by a southern monsoon system similar to the modern I-AM in the middle–late Eocene, although not to the degree experienced by southern Tibet, which hosted greater proportions of forest and was likely more humid (e.g. Jianchuan Basin; Fig. 4). However, it should be borne in mind that rainfall seasonality is not always a proxy for the existence of monsoons; although leaf form is the preferred method for detecting monsoons in deep time climates (Spicer, 2017), the absence of well-preserved fossil leaf assemblages from the Nangqian Basin to date prevents this comparison. Furthermore, palynological records alone are not sufficient for detecting whether the nature of monsoons in the Eocene was more similar to the present I-AM or South Asian monsoon (SAM), which contributes mostly to the moisture in the Nangqian region today (L. Li et al., 2019).
Our results indicate that the brief warming interval recorded in Zone II prompted a considerable change in the vegetation in east-central Tibet, encouraging the temporary spread of (dry) forests in the region, while steppe–desert vegetation contracted. Warming is reflected by an atypical spike in tropical forest, while a warm broad-leaved forest spike in north-eastern Tibet is coincident with the MECO (Hoorn et al., 2012; tropical forest is exceedingly rare in the latter area during the middle–late Eocene). In order to estimate relative humidity in arid environments such as these, the Nitraria / Ephedra (N∕E) ratio can be used to distinguish between desert/semi-desert (<1) and steppe–desert (>1; Li et al., 2005; Hoorn et al., 2012). Although both genera occupy arid environments today, Ephedra is currently distributed primarily throughout deserts, semi-deserts, and grasslands globally (Stanley et al., 2001), while Nitraria is a relatively more humid steppe–desert taxon (Cour et al., 1999; Sun and Wang, 2005; Jiang and Ding, 2008; Li et al., 2009; Zhao and Herzschuh, 2009).
In the RZ section, the proportion of temperate broad-leaved forest in relation to warm broad-leaf and tropical forest became much greater in the upper part (Fig. 3), indicating a cooler climate in the late Eocene, which matches cooling trends recorded by clumped isotopes both in the Nangqian Basin (L. Li et al., 2019) and in the Xining Basin (Page et al., 2019). Importantly, the N∕E ratio in the RZ section is lowest immediately following the warming interval in Zone II (Fig. 3) and persists for an extended period, indicating rapid, prolonged aridification. An overall expansion of steppe–desert vegetation is observed in Zone III, corresponding to patterns observed on the north-eastern TP in the late Eocene (Hoorn et al., 2012; Bosboom et al., 2014). Accordingly, our vegetation results have implications for understanding the importance and extent of aridification across Central Asia in the late Eocene, which was primarily driven by proto-Paratethys Sea regression (Kaya et al., 2019). Ecosystem responses to this event on both the north-eastern and east-central parts of the TP demonstrates that aridification across the Asian continental interior in the late Eocene could have been further-reaching than previously thought. Our findings show that after sea regression, westerly moisture supply carried from the proto-Paratethys Sea was reduced as far as central Tibet. This provides further support for the argument that this sea was a major source of moisture for the Asian interior and, thus, a primary driver of Central Asian climate during the Eocene (Bosboom et al., 2014; Bougeois et al., 2018; Kaya et al., 2019; Meijer et al., 2019).
Long-term aridification in the late Eocene exerted further influence on the vegetational composition in east-central Tibet with regards to the proportions of the ancestral vs. derived types of Ephedripites. In modern and Quaternary settings, this has been developed as a ratio to distinguish between desert and steppe–desert environments, termed the Ephedra fragilis-type sensu lato/Ephedra distachya-type (Ef ∕ Ed) ratio (whereby E. fragilis represents the ancestral type and E. distachya represents the derived type; Fig. 5). Tarasov et al. (1998) found the E. fragilis-type sensu lato to be common in arid climates with mean temperatures of the warmest month above 22 ∘C. Herzschuh et al. (2004) applied the Ef ∕ Ed ratio to Holocene pollen spectra from the Alashan Plateau and tested its reliability with a regional modern pollen dataset, finding Ef ∕ Ed ratios >10 in most samples from desert sites, and values <5 in most samples from the sites with more favourable climates (e.g. forest-steppe, steppe, and alpine meadow).
In the middle–late Eocene of Central Asia, the ancestral type of Ephedripites never comprises more than 25 % of the ephedroid pollen sum in north-eastern Tibet, whereas the derived type makes up at least 60 % (Xining Basin; Han et al., 2016 and Qaidam Basin; Zhu et al., 1985; Miao et al., 2013a; Jiuquan Basin; Miao et al., 2008); this also appears true for north-western Tibet (Tarim Basin; Wang et al., 1990b; Hoh Xil Basin; Miao et al., 2016) and east-central Tibet (Yuan et al., 2017; this study). Therefore, Ef ∕ Ed ratios >10 (supposedly indicative of desert ecosystems) are never observed, despite the N∕E ratio indicating the regular existence of deserts or semi-deserts in northern Tibet (Zhu et al., 1985; Hoorn et al., 2012; Miao et al., 2016), and central Tibet (Yuan et al., 2017; this study) in the Paleogene. Sedimentological evidence suggests the N∕E ratio to be more reliable for these deep time environments, with Nitraria and Ephedra pollen being widely distributed in evaporites and red beds, indicating deposition in arid or semi-arid climates (Sun and Wang, 2005). Therefore, while pollen ratios appear to reflect reliable functions of climate and landscape change for modern and Holocene settings (Li et al., 2010), our results identify possible contradictions between the N∕E and Ef ∕ Ed pollen ratios. This indicates that further verification of these pollen ratios in modern settings and across larger spatial scales is necessary for reliable palaeoenvironmental reconstructions in deep time.
A comparison of palynological assemblages across the Qinghai–Tibetan region indicates that vegetation has changed markedly from the Paleogene to the present (Fig. 4). While the Nangqian region was dominated by steppe–desert shrubs in the past, it now hosts primarily alpine biomes, as do the Hoh Xil and Xining basins. In contrast, the Tarim and Qaidam basins are now significantly more arid than in the Eocene, and forest- and shrub-steppe have been replaced with desert vegetation (Fig. 4). The Jianchuan Basin to the south was dominated by mixed tropical–subtropical coniferous and broad-leaved forest (Wu et al., 2018), and it is also forested today (but with species of a less thermophilic nature). Similarly, the Markam and Gonjo basins host alpine meadow and forest today; although detailed palynological records have not yet been recovered, macrobotanical fossils suggest these areas were dominated by mixed broad-leaved and coniferous forest in the late Eocene–early Oligocene (Su et al., 2018; Studnicki-Gizbert et al., 2008). The above changes indicate that late Paleogene and Neogene topographic growth (creating new high-elevation biomes; Fig. 1a, b), the aridification of inner Asia (Caves et al., 2014, 2016), and global cooling (Zachos et al., 2001; DeConto and Pollard, 2003; Pagani et al., 2011) were all drivers of Cenozoic vegetation shifts across the TP.
5.3 Elevational implications
High-altitude conifers are rare in this particular record, although the high-elevation genus Tsugaepollenites (Fauquette et al., 2006) is present. This could be driven by four possible factors: (1) taphonomy, i.e. the assemblage has a high proportion of autochthonous spores and pollen with little input from the peripheral mountains; (2) the elevation of this region was relatively low in the middle–late Eocene (<3000 m as proposed by Botsyun et al., 2019; also see Wei et al., 2016); (3) due to the generally wetter climate in relation to the north-eastern plateau basins, conifers are not competitive and surrounding mountains are instead forested by temperate angiosperms; and (4) central Tibet recorded regional pollen transported by different atmospheric circulation systems.
Regarding the first possibility, conifers are windblown and can be transported long distances (Lu et al., 2008; Ma et al., 2008; Zhou and Li, 2011); as the region already likely experienced a monsoonal climate (Spicer, 2017; Licht et al., 2014; Caves Rugenstein and Chamberlain, 2018; this study), we consider it unlikely that our assemblages record little to no regional vegetation. The second factor, the elevation history of the TP, is a controversial topic of discussion, and palynological evidence from the RZ section does not provide strong support either for or against a relatively low middle–late Eocene palaeoaltitude in the region. Although the upper part of the RZ section in the Nangqian Basin likely just predates the high-elevation signal further to the north from 37 Ma onwards (Dupont-Nivet et al., 2008; Hoorn et al., 2012; Page et al., 2019), an expanding body of data indicates that a proto-Tibetan highland with complex topography was already in place during the Paleogene (Xu et al., 2013; Ding et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2014; Valdes et al., 2019).
Isotopic evidence suggests moderate to high elevations for the Nangqian Basin in the late Eocene (valley floor 2.7 () km above sea level; surrounding mountains 3.0±1.1 km above sea level; Li L. et al., 2019). In the adjacent Gonjo Basin, stable isotope data suggest the basin had already attained 2100–2500 m palaeoelevation by the early Eocene (Tang et al., 2017). Some of the broad-leaved angiosperms trees present in the new Nangqian assemblage could have grown at maximum elevations of 3600–4000 m during the Eocene (Ilex, Quercus: Song et al., 2010); therefore their presence in lieu of abundant conifers is not in contradiction with an elevated topography in parts of east-central Tibet at this time. This has significance for other Asian palynological studies that infer regional palaeoaltitudes and uplift history of Tibet based solely on palynological records from a single locality: a multi-proxy approach is clearly necessary to address the complex history of Tibetan uplift in future research.
Palynological data from the RZ assemblage supports climate (the third possibility) rather than altitude as a primary driving factor of vegetational composition: locally wetter conditions in the east-central region of the TP (see Sect. 5.2) would likely have promoted angiosperm tree growth over cold-temperate conifers that can withstand drought better, and utilize a winter wet growing season unlike deciduous angiosperms (Dupont-Nivet et al., 2008; Hoorn et al., 2012; Page et al., 2019). The last possibility is also supported, with the palynology of this study suggesting that central Tibet was influenced by two atmospheric circulation systems: predominantly the westerlies from the north (Caves Rugenstein and Chamberlain, 2018), and (to a limited degree) by a southern monsoon, which could conceivably also have transported windblown pollen from subtropical and warm-temperate broad-leaved forests in the south (Su et al., 2018). Today, the Nangqian region receives nearly 70 % of its moisture from the SAM, with the westerlies from the north making up the remainder (Li L. et al., 2019). This indicates that atmospheric circulation systems have changed considerably in east-central Tibet from the Paleogene to Neogene, despite the existence of monsoons in this region since at least the Eocene (Licht et al., 2014; Caves Rugenstein and Chamberlain, 2018; Spicer, 2017). Based on the above, we propose that both local climatic conditions and the influence of different regional atmospheric circulation systems contributed to the development of a unique floral ecosystem in east-central Tibet during the late Eocene.
On the basis of palynological assemblages, we conclude that the rocks of the RZ section (Nangqian Basin) are Bartonian (41.2–37.8 Ma; late Eocene) in age. They record a strongly seasonal steppe–desert ecosystem characterized by Ephedra and Nitraria shrubs, diverse ferns, and an underlying component of broad-leaved forests. The climate became significantly warmer for a short period, encouraging regional forest growth and a proliferation of the thermophilic ancestral Ephedra type but rapidly became more aridified thereafter due primarily to the regression of the proto-Paratethys Sea. This is in conjunction with observed environmental shifts in north-eastern Tibet, suggesting widespread Asian aridification in the late Eocene. A new palynozonation better constrains the biostratigraphy of Paleogene successions across the northern, central, and southern TP, and also illustrates local ecological variability during the Eocene. This highlights the ongoing challenge of integrating various deep time records for the purpose of reconstructing palaeoelevation, and it suggests that a multi-proxy approach is vital for unravelling the complex uplift history of the Qinghai–Tibetan region.
The authors declare that all data supporting the findings of this study are available in the Supplement or are published in a data repository at the following DOI: https://doi.org/10.17632/xvp68wsd2p.4 (Yuan and Barbolini, 2020).
The supplement related to this article is available online at: https://doi.org/10.5194/cp-16-2255-2020-supplement.
QY, VV, FSS, DLG, HCW, and QSF conceptualized the study. QY, FSS, HCW, ZJQ, YSD, and JJS carried out fieldwork. QY, NB, VV, and CR collected and analysed the data. QY wrote the first draft of the paper, and NB, VV, and CR participated in reviewing and editing the final article.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
We thank Fuyuan An (Qinghai Normal University), Shuang Lü (University of Tübingen), and Aijun Sun (University of Chinese Academy of Sciences) for assistance with the fieldwork; Yunfa Miao (Chinese Academy of Sciences) for helpful discussions on the systematic palynology; Luisa Ashworth for lithological identifications; the MAGIC (Monsoons in Asia caused Greenhouse to Icehouse Cooling?) team for fruitful discussions on the topic; and the handling editor Alberto Reyes, as well as two anonymous reviewers, for their constructive comments. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 41302024 to Qin Yuan); the Youth Guiding Fund of Qinghai Institute of Salt Lakes, CAS (grant no. Y360391053 to Qin Yuan); the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research Program (STEP) CAS (grant no. 2019 QZKK0805 to Qin Yuan), and the Swedish Research Council (Vetenskapsrådet; grant no. VR 2019-4061 to Vivi Vajda and grant no. VR 2017-03985 to Catarina Rydin). The funding sources had no involvement in the study design.
This research has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 41302024); the Youth Guiding Fund of Qinghai Institute of Salt Lakes, CAS (grant no. Y360391053); the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research Program (STEP) CAS (grant no. 2019 QZKK0805); and the Vetenskapsrådet (grant nos. VR 2019-4061 and VR 2017-03985).
The article processing charges for this open-access
publication were covered by Stockholm University.
This paper was edited by Alberto Reyes and reviewed by two anonymous referees.
Abels, H. A., Dupont-Nivet, G., Xiao, G., Bosboom, R., and Krijgsman, W.: Step-wise change of Asian interior climate preceding the Eocene-Oligocene Transition (EOT), Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl., 299, 399–412, 2011.
Aitchison, J. C. and Davis, A. M.: When did the India-Asia collision really happen?, Gondwana. Res., 4, 560–561, 2001.
Aitchison, J. C., Xia, X. P., Baxter, A. T., and Ali, J. R.: Detrital zircon U-Pb ages along the Yarlung-Tsangpo suture zone, Tibet: implications for oblique convergence and collision between India and Asia, Gondwana. Res., 20, 691–709, 2011.
Baumann, F., He, J. S., Scheidt, K., Kühn, P., and Scholten, T.: Pedogenesis, permafrost, and soil moisture as controlling factors for soil nitrogen and carbon contents across the Tibetan Plateau, Glob. Change Biol., 15, 3001–3017, 2009.
Bolinder, K., Norbäck Ivarsson, L., Humphreys, A. M., Ickert-Bond, S. M., Han, F., Hoorn, C., and Rydin, C.: Pollen morphology of Ephedra (Gnetales) and its evolutionary implications, Grana, 55, 24–51, 2016.
Bosboom, R. E., Dupont-Nivet, G., Houben, A. J. P., Brinkhuis, H., Villa, G., Mandic, O., Stoica, M., Zachariasse, W. J., Guo, Z. J, Li, C. X, and Krijgsman, W.: Late Eocene sea retreat from the Tarim Basin (west China) and concomitant Asian paleoenvironmental change, Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl., 299, 385–398, 2011.
Bosboom, R. E., Abels, H. A., Hoorn, G., Van den Berg, B. C. J., Guo, Z. J., and Dupont-Nivet, G.: Aridification in continental Asia after the Middle Eocene Climatic Optimum (MECO), Earth Planet. Sc. Lett., 389, 34–42, 2014.
Botsyun, S., Sepulchre, P., Donnadieu, Y., Risi, C., Licht, A., and Caves Rugenstein, J.: Revised paleoaltimetry data show low Tibetan Plateau elevation during the Eocene, Science, 363, eaaq1436, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaq1436, 2019.
Bougeois, L., Dupont-Nivet, G., De Rafélis, M., Tindall, J., Proust, J. N., Reichart, G. J., Nooijer, L., Guo, Z. J., and Ormukov, C.: Asian monsoons and aridification response to Paleogene sea retreat and Neogene westerly shielding indicated by seasonality in Paratethys oysters, Earth Planet. Sc. Lett., 485, 99–110, 2018.
Cai, M. T., Fang, X. M., Wu, F. L., Miao, Y. F., and Appel, E.: Pliocene-Pleistocene stepwise drying of Central Asia: evidence from paleo-magnetism and sporopollen record of the deep borehole SG-3 in the western Qaidam Basin, NE Tibetan Plateau, Global Planet Change, 94–95, 72–81, 2012.
Cavalli-Sforza, L. L. and Edwards, A. W.: Phylogenetic analysis. Models and estimation procedures, Am. J. Hum. Genet., 19, p. 233, 1967.
Caves, J. K., Sjostrom, D. J., Mix, H. T., Winnick, M. J., and Chamberlain, C. P.: Aridification of Central Asia and uplift of the Altai and Hangay Mountains, Mongolia: Stable isotope evidence, Am. J. Sci., 314, 1171–1201, 2014.
Caves, J. K., Winnick, M. J., Graham, S. A., Sjostrom, D. J., Mulch, A., and Chamberlain, C. P.: Role of the westerlies in Central Asia climate over the Cenozoic, Earth Planet. Sc. Lett., 428, 33–43, 2015.
Caves, J. K., Moragne, D. Y., Ibarra, D. E., Bayshashov, B. U., Gao, Y., Jones, M. M., Zhamangara, A., Arzhannikova, A. V., Arzhannikov, S. G., and Chamberlain, C. P.: The Neogene de-greening of Central Asia, Geology, 44, 887–890, 2016.
Caves Rugenstein, J. K. and Chamberlain, C. P.: The evolution of hydroclimate in Asia over the Cenozoic: A stable-isotope perspective, Earth-Sci. Rev., 185, 1129–1156, 2018.
Cour, P., Zheng, Z., Duzer, D., Calleja, M., and Yao, Z.: Vegetational and climatic significance of modern pollen rain in northwestern Tibet, Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol., 104, 183–204, 1999.
DeConto, R. M. and Pollard, D.: Rapid Cenozoic glaciation of Antarctica induced by declining atmospheric CO2, Nature, 421, 245–249, 2003.
Deng, W., Sun, H., and Zhang, Y.: Cenozoic K-Ar ages of volcanic rocks in the Nangqian Basin, Qinghai, Chinese Sci. Bull., 44, 2554–2558, 1999 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ding, L., Xu, Q., Yue, Y. H., Wang, H. Q., Cai, F. I., and Li, S.: The Andean-type Gangdese Mountains: paleoelevation record from the Paleocene-Eocene Linzhou Basin, Earth Planet. Sc. Lett., 392, 250–264, 2014.
Du, H. F., Jiang, Y. B., Yan, Z. B., Hou, Z. Q., Yang, T. N., Guo, F. S., and Yang, Q. K.: Sedimentary Characteristics and Environment of the Paleogene Nangqian Basin in Qinghai Province, Acta Geol. Sin., 85, 383–395, 2011 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Dupont-Nivet, G., Keijgsman, W., Langereis, C. G., Abels, H. A., Dai, S., and Fang, X. M.: Tibetan plateau aridification linked to global cooling at the Eocene-Oligocene transition, Nature, 445, 635–638, 2007.
Dupont-Nivet, G., Hoorn, C., and Konert, M.: Tibetan uplift prior to the Eocene-Oligocene climate transition: evidence from pollen analysis of the Xining Basin, Geology, 36, 987–990, 2008.
Fauquette, S., Suc, J. P., Bertini, A., Popescu, S. M., Warny, S., Taoufiq, N. B., Villa, M. J. P., Chikhi, H., Feddi, N., Subally, D., and Clauzon, G.: How much did climate force the Messinian salinity crisis? Quantified climatic conditions from pollen records in the Mediterranean region, Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl., 238, 281–301, 2006.
Grimm, E. C.: CONISS: a FORTRAN 77 program for stratigraphically constrained cluster analysis by the method of incremental sum of squares, Comput. Geosci. UK, 13, 13–35, 1987.
Grimm, E. C.: TILIA v2. 0. b. 4 and TGView v2. 0 (computer software), Illinois State Museum, Research and Collections Center, Springfield, IL, USA, available at: https://tiliait.com/ (last access: 18 November 2020), 1991.
Gupta, A. K., Singh, R. K., Joseph, S., and Thomas, E.: Indian Ocean high-productivity event (10–8 Ma): Linked to global cooling or to the initiation of the Indian monsoons?, Geology, 32, 753–756, 2004.
Han, F., Rydin, C., Bolinder, K., Dupont-Nivet, G., Abels, H. A., Koutsodendris, A., Zhang, K., and Hoorn, C.: Steppe development on the Northern Tibetan Plateau inferred from Paleogene ephedroid pollen, Grana, 55, 71–100, 2016.
Herb, C., Koutsodendris, A., Zhang, W. L., Appel, E., Fang, X. M., Voigt, S., and Pross, J.: Late Plio-Pleistocene humidity fluctuations in the western Qaidam Basin (NE Tibetan Plateau) revealed by an integrated magnetic-palynological record from lacustrine sediments, Quat. Res., 84, 457–466, 2015.
Herzschuh, U.: Reliability of pollen ratio for environmental reconstructions on the Tibetan Plateau, J. Biogeogr., 34, 1265–1273, 2007.
Herzschuh, U., Tarasov, P., Wünnemann, B., and Hartmann, K., Holocene vegetation and climate of the Alashan Plateau NW China, reconstructed from pollen data, Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl., 211, 1–17, 2004.
Hoorn, C., Straathof, J., Abels, H. A., Xu, Y. D., Utescher, T., and Dupont-Nivet, G.: A late Eocene palynological record of climate change and the Tibetan Plateau uplift (Xining Basin, China), Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl., 344, 16–38, 2012.
Horton, B. K., Yin, A., Spurlin, M. S., Zhou, J., and Wang, J.: Paleocene-Eocene syncontractional sedimentation in narrow, lacustrine-dominated basins of east-central Tibet, Geol. Soc. Am. Bull., 114, 771–786, 2002.
Hou, Z., Hongwen, M., Zaw, K., Yuquan, Z., Mingjie, W., Zeng, W., Guitang, P., and Renli, T.: The Himalayan Yulong porphyry copper belt: product of large-scale strike-slip faulting in eastern Tibet, Econ. Geol., 98, 125–145, 2003.
Hu, X. M., Garzanti, E., Wang, J. G., Huang, W. T., An, W., and Webb, A.: The timing of India-Asia collision onset – Facts, theories, controversies, Earth-Sci. Rev., 160, 264–299, 2016.
Ji, L. M., Meng, F. W., Yan, K., and Song, Z. G.: The dinoflagellate cyst Sub-tilisphaera from the Eocene of the Qaidam Basin, northwest China, and its implications for hydrocarbon exploration, Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol., 167, 40–50, 2011.
Jiang, H. and Ding, Z.: A 20 Ma pollen record of East-Asian summer monsoon evolution from Guyuan, Nigxia, China, Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl., 265, 30–38, 2008.
Jiang, Y. B., Guo, F. S., Hou, Z. Q., Yang, T. N., Liu, Y. X., Yang, Q. K., and Du, H. F.: Sedimentary features and evolution of the Nangqian Paleogene basin in northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, Acta Petrol. Et. Miner., 30, 391–400, 2011 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Jin, C., Liu, Q., Liang, W., Roberts, A. P., Sun, J., Hu, P., Zhao, X., Su, Y., Jiang, Z., Liu, Z., and Duan, Z.: Magnetostratigraphy of the Fenghuoshan Group in the Hoh Xil Basin and its tectonic implications for India-Eurasia collision and Tibetan Plateau deformation, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 486, 41–53, 2018.
Kaya, M. Y., Dupont-Nivet, G., Proust, J-N., Roperch, P., Bougeois, L., Meijer, N., Frieling, J., Fioroni, C., Altiner, S. Ö., Vardar, E., Barbolini, N., Stoica, M., Aminov, J., Mamtimin, M., and Guo, Z.: Paleogene evolution and demise of the proto-Paratethys Sea in Central Asia (Tarim and Tajik basins): role of intensified tectonic activity at ∼41 Ma, Basin Res., 31, 461–486, 2019.
Kotthoff, U., Greenwood, D. R., McCarthy, F. M. G., Müller-Navarra, K., Prader, S., and Hesselbo, S. P.: Late Eocene to middle Miocene (33 to 13 million years ago) vegetation and climate development on the North American Atlantic Coastal Plain (IODP Expedition 313, Site M0027), Clim. Past, 10, 1523–1539, https://doi.org/10.5194/cp-10-1523-2014, 2014.
Li, Y., Xu, Q., Zhao, Y., Yang, X., Xiao, J., Chen, H., and Lü, X.: Pollen indication to source plants in the eastern desert of China, Chinese Sci. Bull., 50, 1632–1641, 2005.
Li, J. G., Batten, D. J., and Zhang, Y. Y.: Palynological indications of environmental changes during the Late Cretaceous-Eocene on the southern continental margin of Laurasia, Xizang (Tibet), Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl., 265, 78–86, 2008.
Li, Y., Wang, N., Morrill, C., Cheng, H., Long, H., and Zhao, Q.: Environmental change implied by the relationship between pollen assemblages and grain-size in N.W., Chinese lake sediments since the Late Glacial, Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol., 154, 54–64, 2009.
Li, F., Sun, J., Zhao, Y., Guo, X., Zhao, W., and Zhang, K.: Ecological significance of common pollen ratios: A review Front, Earth Sci. Chin., 4, 253–258, 2010.
Li, S. Y., Currie, B. S., Rowley, D. B., and Ingalls, M.: Cenozoic paleoaltimetry of the SE margin of the Tibetan Plateau: Constraints on the tectonic evolution of the region, Earth Planet. Sc. Lett., 432, 415–424, 2015.
Li, X., Zhang, R., Zhang, Z., and Yan, Q.: What enhanced the aridity in Eocene Asian inland: Global cooling or early Tibetan Plateau uplift? Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl., 510, 6–14, 2018.
Li, J. G., Wu, Y. X., Batten, D. J., and Lin, M. Q.: Vegetation and climate of the central and northern Qinghai-Xizang plateau from the Middle Jurassic to the end of the Paleogene inferred from palynology, J. Asian Earth Sci., 175, 34–38, 2019.
Li, L., Fan, M., Davila, N., Jesmok, G., Mitsunaga, B., Tripati, A., and Orme, D.: Carbonate stable and clumped isotopic evidence for late Eocene moderate to high elevation of the east-central Tibetan Plateau and its geodynamic implications, GSA Bulletin, 131, 831–844, 2019.
Li, J. F., Xie, G., Yang, J., Ferguson, D. K., Liu, X. D., Liu, H., and Wang, Y. F.: Asian Summer Monsoon changes the pollen flow on the Tibetan Plateau, Earth-Sci. Rev., 202, 103–114, 2020.
Licht, A., Cappelle, M. V., Ables, H. A., Ladant, J. B., Trabucho-Alexandre, J., France-Lanord, C., Donnadieu, Y., Vandenberghe, J., Rigaudier, T., Lecuyer, C., Terry Jr., D., Adriaens, R., Boura, A., Guo, Z., Soe, A. N., Quade, J., Dupont-Nivet, G., and Jaeger, J. J.: Asian monsoons in a late Eocene greenhouse world, Nature, 513, 501–506, 2014.
Linnemann, U., Su, T., Kunzmann, L., Spicer, R. A., Ding, W. N., Spicer, T. E. V., Zieger, J., Hofmann, M., Moraweck, K., Gärtner, A., and Gerdes, A.: New U-Pb dates show a Paleogene origin for the modern Asian biodiversity hot spots, Geology, 46, 3–6, 2018.
Liu, G. W.: Fupingopollenites gen. nov. and its distribution, Acta Palaeontol. Sin., 24, 64–70, 1985 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, Z. Q.: Geologic map of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau and its neighboring regions: Beijing, Chengdu Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources, Geologic Publishing House, scale 1:1 500 000, 1988.
Liu, J., Li, J. J., Song, C. H., Yu, H., Peng, T. J., Hui, Z. C., and Ye, X. Y.: Palynological evidence for late Miocene stepwise aridification on the northeastern Tibetan Plateau, Clim. Past, 12, 1473–1484, https://doi.org/10.5194/cp-12-1473-2016, 2016.
Liu, Y., Liu, H., Theye, T., and Massonne, H. J.: Evidence for oceanic subduction at the NE Gondwana margin during Permo-Triassic times, Terra Nova, 21, 195–202, 2009.
Liu, Z., Zhao, X., Wang, C. S., and Liu, H. Y.: Magnetostratigraphy of Tertiary sediments from the Hoh Xil Basin: implications for the Cenozoic tectonic history of the Tibetan Plateau, J. Asian Earth Sci., 154, 233–252, 2003.
Lu, H., Wu, N., Yang, X., Shen, C., Zhu, L., Wang, L., Li, Q., Xu, D., Tong, G., and Sun, X.: Spatial patterns of Abies and Picea surface pollen distribution along the elevation gradient in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and Xinjiang, China, Boreas, 37, 254–262, 2008.
Lu, J. F., Song, B. W., Chen, R. M., Zhang, J. Y., and Ye, H.: Palynological assemblage of Eocene-Oligocene pollen and their biostratigraphic correlation in Dahonggou, Daqaidam Regions, Qaidam Basin, Earth Sci. J. China University of Geosciences, 35, 839–848, 2010 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ma, Y., Liu, K., Feng, Z., Sang, Y., Wang, W., and Sun, A.: A survey of modern pollen and vegetation along a south-north transect in Mongolia, J. Biogeogr., 35, 1512–1532, 2008.
Mao, Y. B.: Tectonic evolvement Coal accumulation in Zaduo-Nangqian area of Qinghai Province, J. Earth Sci. Environ., 32, 225–233, 2010 (in Chinese).
Meijer, N., Dupont-Nivet, G., Abels, H. A., Kaya, M. Y., Licht, A., Xiao, M. M., Zhang, Y., Roperch, P., Poujol, M., Lai, Z. P., and Guo, Z. J.: Central Asian moisture modulated by proto-Paratethys Sea incursions since the early Eocene, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 510, 73–84, 2019.
Miao, Y. F.: Cenozoic Pollen Records in the Xining Basin and Its Significance for the Palaeoclimate Change, Postdoctoral Report, Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 95 pp., 2010 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Miao, Y. F., Fang, X. M., Song, Z. C., Wu, F. L., Han, W. X., Dai, S., and Song, C. H.: Late Eocene pollen records and paleoenvironmental changes in northern Tibetan Plateau, Sci. China Earth Sci., 51, 1089–1098, 2008.
Miao, Y. F., Fang, X. M., Herrmann, M., Wu, F. L., Zhang, Y. Z., and Liu, D. L.: Miocene pollen record of KC-1 core in the Qaidam Basin, NE Tibetan Plateau and implications for evolution of the East Asian monsoon, Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl., 299, 30–38, 2011.
Miao, Y. F., Herrmann, M., Wu, F. L., Yan, X. L., and Yang, S. L.: What controlled Mid-Late Miocene long-term aridification in Central Asia? Global cooling or Tibetan Plateau uplift: a review, Earth Sci. Rev., 112, 155–172, 2012.
Miao, Y. F., Fang, X. M., Wu, F. L., Cai, M. T., Song, C. H., Meng, Q. Q., and Xu, L.: Late Cenozoic continuous aridification in the western Qaidam Basin: evidence from sporopollen records, Clim. Past, 9, 1863–1877, https://doi.org/10.5194/cp-9-1863-2013, 2013a.
Miao, Y. F., Fang, X. M., Song, C. H., Yan, X. L., Xu, L., and Chen, C. F.: Pollen and fossil wood's linkage with Mi-1 Glaciation in northeastern Tibetan Plateau, China, Palaeoworld, 22, 101–108, 2013b.
Miao, Y. F., Wu, F. L., Chang, H., Fang, X. M., Deng, T., Sun, X. M., and Jin, C. S.: A Late Eocene palynological record from the Hoh Xil Basin, Northern Tibetan Plateau, and its implications for stratigraphic age, paleoclimate and paleoelevation, Gondwana Res., 31, 241–252, 2016.
Molnar, P.: Late Cenozoic increase in accumulation rates of terrestrial sediments: How might climate change have affected erosion rates?, Annu. Rev. Earth Pl. Sc., 32, 67–89, 2004.
Molnar, P. and Tapponnier, P.: Effects of a Continental Collision, Science, 189, 419–426, 1975.
Molnar, P., Boos, W. R., and Battisti, D. S.: Orographic controls on climate and paleoclimate of Asia: thermal and mechanical roles for the Tibetan Plateau, Annu. Rev. Earth Pl. Sc., 38, 77–102, 2010.
Mulch, A. and Chamberlain, C. P.: The rise and growth of Tibet, Nature, 439, 670–671, 2006.
Paeth, H., Steger, C., Li, J. M., Mutz, S. G., and Ehlers, T. A.: Comparison of Cenozoic surface uplift and glacial-interglacial cycles on Himalaya-Tibet paleo-climate: Insights from a regional climate model, Global Planet. Change, 177, 10–26, 2019.
Pagani, M., Hubei, M., Liu, Z. H., Bohaty, S. M., Henderikes, J., Sijp, W., Krishnan, S., and DeConto, R. M.: The role of carbon dioxide during the onset of Antarctic glaciation, Science, 334, 1261–1264, 2011.
Page, M., Licht, A., and Dupont-Nivet, G.: Synchronous cooling and decline in monsoonal rainfall in northeastern Tibet during the fall into the Oligocene icehouse, Geology, 47, 203–206, 2019.
Qinghai BGMR, (Qinghai Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources): Geologic map of the Nangqian region, with geologic report, unpublished, 198 pp., scale 1 : 200 000, 1983a.
Qinghai BGMR (Qinghai Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources): Geologic map of the Shanglaxiu region, with geologic report: unpublished, 220 pp., scale 1 : 200 000, 1983b.
Qinghai BGMR (Qinghai Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources): Regional Geology of Qinghai Province, Geological Publishing House, Beijing, China, 66 pp., 1991.
Rowley, D. B. and Currie, B. S.: Palaeo-altimetry of the late Eocene to Miocene Lunpola basin, central Tibet, Nature, 439, 677–681, 2006.
Shen, H. and Poulsen, C. J.: Precipitation δ18O on the Himalaya–Tibet orogeny and its relationship to surface elevation, Clim. Past, 15, 169–187, https://doi.org/10.5194/cp-15-169-2019, 2019.
Song, Z. C. and Liu, G. W.: Early Tertiary palynoflora and its significance of palaeogeography from northern and eastern Xizang, in: Integrative Scientific Expedition Team to the Qinghai-Xizang plateau, edited by: Academia Sinica, Palaeontology of Xizang, Book V, Science Press, Beijing, China, 183–201, 1982 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Song, X. Y., Spicer, R. A., Yan, J., Yao, Y. F., and Li, C. S.: Pollen evidence for an Eocene to Miocene elevation of central southern Tibet predating the rise of the High Himalaya, Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl., 297, 159–168, 2010.
Spicer, R. A.: Tibet, the Himalaya, Asian monsoons and biodiversity in what ways are they related?, Plant Diversity, 39, 233–244, 2017.
Spicer, R. A., Su, T., Valdes, P. J., Farnsworth, A., Wu, F. X., Shi, G., Spicer, T. E., and Zhou, Z.: Why the “Uplift of the Tibetan Plateau” is a myth, Natl. Sci. Rev., nwaa091, https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwaa091, online first, 2020.
Spurlin, M. S., Yin, A., Horton, B. K., Zhou, J., and Wang, J.: Structural evolution of the Yushu-Nangqian region and its relationship to syncollisional igneous activity, east-central Tibet, Geol. Soc. Am. Bull., 117, 1293–1317, 2005.
Stanley, C., Charlet, D. A., Freitag, H., Maier-Stolte, M., and Starratt, A. N.: New observations on the secondary chemistry of world Ephedra (Ephedraceae), Am. J. Bot., 88, 1199–1208, 2001.
Studnicki-Gizbert, C., Burchfiel, B. C., Li, Z., and Chen, Z.: Early Tertiary Gonjo basin, eastern Tibet: Sedimentary and structural record of the early history of India-Asia collision, Geosphere, 4, 713–735, 2008.
Su, T., Spicer, R. A., Li, S. H., Huang, J., Sherlock, S., Huang, Y. J., Li, S. F., Wang, L., Jia, L. B., Deng, W. Y. D., Liu, J., Deng, C. L., Zhang, S. T., Valdes, P. J., and Zhou, Z. K.: Uplift, climate and biotic changes at the Eocene-Oligocene transition in south-eastern Tibet, Natl. Sci. Rev., 6, 495–504, 2018.
Su, T., Farnsworth, A., Spicer, R. A., Huang, J., Wu, F. X., Liu, J., Li, S. F., Xing, Y. W., Huang, Y. J., Deng, W. Y. D., Tang, H., Xu, C. L., Zhao, F., Srivastava, G., Valdes, P. J., Deng, T., and Zhou, Z. K.: No high Tibetan Plateau until the Neogene, Science Advances, 5, 1–8, 2019.
Sun, X. J. and Wang, P. X.: How old is the Asian monsoon system-palaeobotanical records from China, Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl., 222, 181–222, 2005.
Sun, Z. C., Feng, X. J., Li, D. M., Yang, F., Qu, Y. H., and Wang, H. J.: Cenozoic Ostracoda and palaeoenvironments of the northeastern Tarim Basin western China, Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl.148, 37–50, 1999.
Sun, Z., Yang, Z. Y., Pei, X. H., Wang, X. S., Yang, T. S., Li, W. M., and Yuan, S. H.: Magnetostratigraphy of Paleogene sediments from northern Qaidam Basin, China: implications for tectonic uplift and block rotation in northern Tibetan plateau, Earth Planet. Sc. Lett., 237, 635–646, 2005.
Tang, M., Liu-Zeng, J., Hoke, G. D., Xu, Q., Wang, W., Li, Z., Zhang, J., and Wang, W.: Paleoelevation reconstruction of the Paleocene-Eocene Gonjo basin, SE-central Tibet, Tectonophysics, 712, 170–181, 2017.
Tarasov, P. E., Cheddadi, R., Guiot, J., Bottema, S., Peyron, O., Belmonte, J., Ruiz-sanchez, V., Saadi, F., and Brewer, S.: A method to determine warm and cool steppe biomes from pollen data; application to the Mediterranean and Kazakhstan regions, J. Quaternary Sci., 13, 335–344, 1998.
Tardif, D., Fluteau, F., Donnadieu, Y., Le Hir, G., Ladant, J.-B., Sepulchre, P., Licht, A., Poblete, F., and Dupont-Nivet, G.: The origin of Asian monsoons: a modelling perspective, Clim. Past, 16, 847–865, https://doi.org/10.5194/cp-16-847-2020, 2020.
Valdes, P. J., Lin, D., Farnsworth, A., Spicer, R. A., Li, S. H., and Tao, S.: Comment on “Revised paleoaltimetry data show low Tibetan Plateau elevation during the Eocene”, Science, 365, eaax8474, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aax8474, 2019.
Wang, Z.: A new Permian gnetalean cone as fossil evidence for supporting current molecular phylogeny, Ann. Bot., 94, 281–288, 2004.
Wang, D., Sun, X. Y., and Zhao, Y.: Late Cretaceous to Tertiary palynofloras in Xingjiang and Qinghai China, Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol., 65, 95–104, 1990a.
Wang, D., Sun, X. Y., Zhao, Y., He, Z.: Palynoflora from Late Cretaceous to Tertiary in Some Regions of Qinghai and Xinjiang, China Environmental Science Press, Beijing, China, 1–179, 1990b (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang, J., Wang, Y. J., Liu, Z. C., Li, J. Q., and Xi, P.: Cenozoic environmental evolution of the Qaidam Basin and its implications for the uplift of the Tibetan Plateau and the drying of central Asia, Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl., 152, 37–47, 1999.
Wang, S. F., Yi, H. S., and Wang, C. S.: Sedimentary facies and palaeogeography features of Nangqian Tertiary basin in Yushu district, Qinghai, Northwestern Geol., 34, 64–67, 2001. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang, S. F., Yi, H. S., and Wang, C. S.: Sediments and structural features of Nangqian Tertiary Basin in eastern of Tibet-Qingzang Plateau, Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin., 38, 109–114, 2002 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang, C. S., Zhao, X. X., Liu, Z. Z., Peter, C., Stephan, A. G., Robert, S. C., Zhu, L. D., Liu, S., and Li, Y. L.: Constraints on the early uplift history of the Tibetan Plateau, P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 105, 4987–4992, 2008.
Wang, C. W., Hong, H. L., Li, Z. H., Yin, K., Xie, J., Liang, G. J., Song, B., Song, E., Zhang, K. X.: The Eocene-Oligocene climate transition in the Tarim Basin, Northwest China: evidence from clay mineralogy, Appl. Clay. Sci., 74, 10–19, 2013.
Wang C. S., Dai, J. G., Zhao, X. X., Li, Y. L., Graham, S. A., He, D. F., Ran, B., and Meng, J.: Outward-growth of the Tibetan Plateau during the Cenozoic: A review, Tectonophysics, 621, 1–43, 2014.
Wang, Z., Shen, Y., and Pang, Z.: Three main stages in the uplift of the Tibetan Plateau during the Cenozoic period and its possible effects on Asian aridification: A review, Clim. Past Discuss., https://doi.org/10.5194/cp-2018-64, 2018.
Wei, M.: Eogene ostracods from Nangqen in Qinghai. Contribution to the Geology of the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau, Geological Publishing House, Beijing, China, 17, 313–324, 1985 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wei, H. C., Fan, Q. S., Zhao, Y., Ma, H. Z., Shan, F. S., An, F. Y., and Yuan, Q.: A 94–10 Ka pollen record of vegetation change in Qaidam Basin, northeastern Tibetan Plateau, Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl., 431, 43–52, 2015.
Wei, Y., Zhang, K., Garzione, C. N., Xu, Y. D., Song, B., and Ji, J. L.: Low palaeoelevation of the northern Lhasa terrane during late Eocene: Fossil foraminifera and stable isotope evidence from the Gerze Basin, Sci. Rep., 6, 27508, https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27508, 2016.
Wu, J., Zhang, K., Xu, Y., Wang, G., Garzione, C. N., Eiler, J., Leloup, P. H., Sorrel, P., and Mahéo, G.: Paleoelevations in the Jianchuan Basin of the southeastern Tibetan Plateau based on stable isotope and pollen grain analyses, Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl., 510, 93–108, 2018.
Xia, L. Q., Li, X. G., Ma, Z. P., Xu, X. Y., and Xia, Z. C.: Cenozoic volcanism and tectonic evolution of the Tibetan plateau, Gondwana Res., 19, 850–866, 2011.
Xiao, G. Q., Abels, H. A., Yao, Z. Q., Dupont-Nivet, G., and Hilgen, F. J.: Asian aridification linked to the first step of the Eocene-Oligocene climate Transition (EOT) in obliquity-dominated terrestrial records (Xining Basin, China), Clim. Past, 6, 501–513, https://doi.org/10.5194/cp-6-501-2010, 2010.
Xu, R., Song, Z. C., and Zhou, H. Y., The palynological assemblages in Tertiary sediments of Qaidam Basin and its significance in geology, Acta. Palaeontol. Sin., 6, 429–440, 1958 (in Chinese).
Xu, Q., Ding, L., Zhang, L. Y., Cai, F. L., Lai, Q. Z., Yang, D., and Zeng, J. L.: Paleogene high elevations in the Qiangtang Terrane, central Tibetan Plateau, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 362, 31–42, 2013.
Xu, Y., Bi, X. W., Hu, R. Z., Chen, Y. W., Liu, H. Q., and Xu, L. L.: Geochronology and geochemistry of Eocene potassic felsic intrusions in the Nangqian basin, eastern Tibet: Tectonic and metallogenic implications, Lithos, 246–247, 212–227, 2016.
Yang, Y.: Systematic and Evolution of Ephedra L. (Ephedraceae) from China, PhD Thesis, Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 231 pp., 2002 (in Chinese with English summary).
Yin, A. and Harrison, T. M.: Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogeny, Annu. Rev. Earth Pl. Sc., 28, 211–280, 2000.
Yuan, Q. and Barbolini, N.: “Supplementary dataset: Aridification signatures from middle-late Eocene pollen indicate widespread drying across the Tibetan Plateau after 40 Ma”, Mendeley Data, v4, https://doi.org/10.17632/xvp68wsd2p.4, 2020.
Yuan, Q., Vajda, V., Li., Q. K., and Shan, F. S.: A late Eocene palynological record from the Nangqian Basin, Tibetan Plateau: Implications for stratigraphy and paleoclimate, Palaeoworld, 26, 369–379, 2017.
Yuan, Q., Barbolini, N., Ashworth, L., Rydin, C., Gao, D. L., Wei, H. C., Fan, Q. S., Qin, Z. J., Du, Y. S., Shan, J. J., Shan, F. S., and Vajda, V.: Palaeoenvironmental changes in Eocene Tibetan lake systems traced by geochemistry, sedimentology and palynofacies, J. Asian Earth Sci., in review, 2020.
Zachos, J., Pagani, M., Sloan, L., Thomas, E., and Billups, K.: Trends, rhythms, and aberrations in global climate 65 Ma to present, Science, 292, 686–693, 2001.
Zhang, W. L.: The high precise Cenozoic magnetostratigraphy of the Qaidam Basin and uplift of the Northern Tibetan plateau, (PhD Thesis), Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 109 pp., 2006.
Zhang, J., Santosh, M., Wang, X., Guo, L., Yang, X., and Zhang, B.: Tectonics of the northern Himalaya since the India-Asia collision, Gondwana Res., 21, 939–960, 2012.
Zhao, Y. and Herzschuh, U.: Modern pollen representation of source vegetation in the Qaidam Basin and surrounding mountains, north-eastern Tibetan Plateau, Veg. Hist. Archaeobot., 18, 245–260, 2009.
Zhou, X. Y. and Li, X. Q.: Variations in spruce (Picea sp.) distribution in the Chinese Loess Plateau and surrounding areas during the Holocene, Holocene, 22, 687–696, 2011.
Zhu, Z. H., Wu, L., Xi, P., Song, Z. C., and Zhang, Y. Y.: A Research on Tertiary Palynology from the Qaidam Basin, Qinghai Province, Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing, China, 1–297, 1985 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhu, H. C., Ouyang, S., Zhan, J. Z., and Wang, Z.: Comparison of Permian palynological assemblages from the Junggar and Tarim Basins and their phytoprovincial significance, Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol, 136, 181–207, 2005.
Zhu, L., Zhang, H. H., Wang, J. H., Zhou, J. Y., and Xie, G. H.: 40Ar∕39Ar chronology of high-K magmatic rocks in Nangqian Basin at the northern segment of the Jinsha-Red River Shear Zone (JRRSZ), Geotecton. et Metallog., 30, 241–247, 2006 (in Chinese with English abstract).





